
Overlap is above and below the bond axis, not directly between the bonded atoms. energy of isolated p orbitals bond order of a pi bond = (2)-(0) 2 = 1 bond 2p b π * = 2p a-2p b = antibonding MO = LCAO = linear combination of atomic orbitals ∆E = bond energy There is a big energy advantage for a pi bond over two isolated p orbitals. Problem 1 – What would the MO pictures of He 2, H 2 +, H 2-and He 2 + look like? Would you expect that these species could exist? What would be their bond orders? node = zero electron density because of opposite phases 2p a π bond LUMO HOMO π = 2p a + 2p b = bonding MO = potential energy higher, less stable lower, more stable LUMO = lowest unoccupied molecular orbital HOMO = highest occupied molecular orbital Similar phase of electron density (no node) adds together constructively. There is a node between the bonding atoms (zero electron density). Sigma star (σ*) antibonding molecular orbital – Normally this orbital is empty, but if it should be occupied, the wave nature of electron density (when present) is out of phase (destructive interference) and canceling in nature. A pi bond is a weaker chemical covalent bond than a sigma bond (since bonds have a smaller overlap between the orbitals), but when it is put with a sigma bond it creates a much stronger hold between the atoms, thus double and triple bonds are stronger then single bonds.The pi bond looks like two macaronis sandwiching the sigma bond. A sigma bonds is always the first bond formed between two atoms.
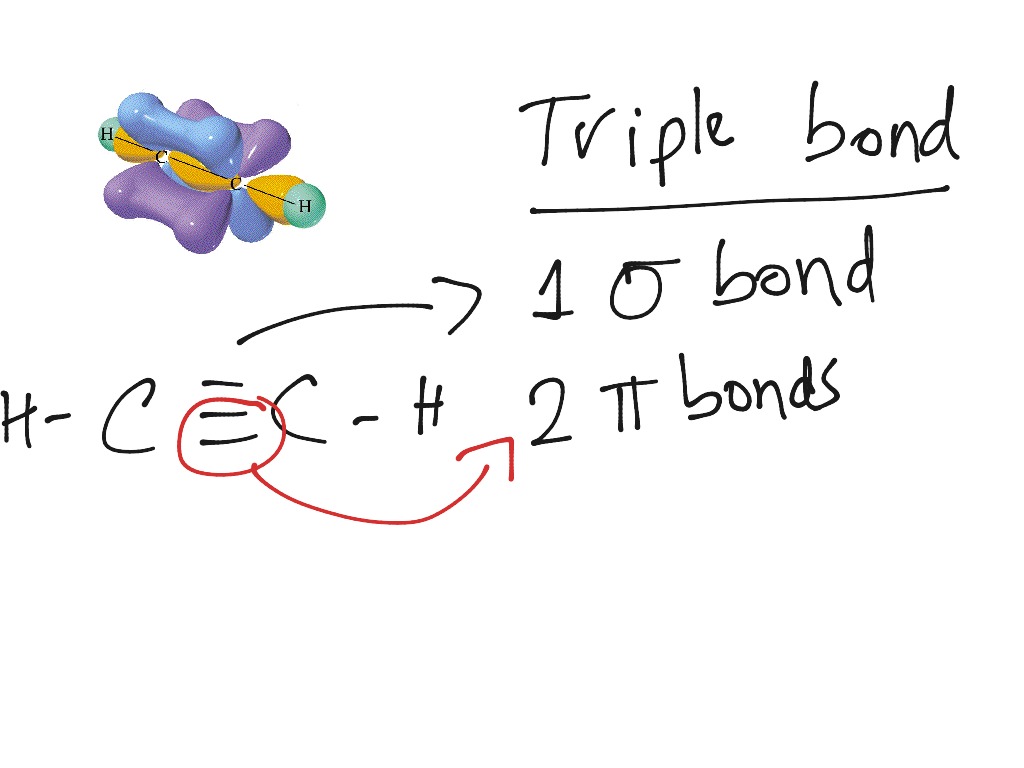
Explain the shape of ethane molecule in terms of sigma and pi C-C bonds. In terms of bond order, single bonds have one sigma bond, double bonds consist of one sigma bond and one pi bond, and triple bonds contain one sigma bond and two pi bonds. Discuss the examples of carnivorous plants (pitcher plant, venus fly trap. For example, a bond between two s-orbital electrons is a sigma bond, because two spheres are always coaxial. The sp2 hybrid orbitals are purple and the pz orbital is blue. Pi bonds occur when two orbitals overlap when they are parallel.

The figure below shows the two types of bonding in C 2H 4.
Sigma (σ) bonding molecular orbital-Shared electron density is directly between the bonding atoms, along the bonding axis. A pi bond ( bond) is a bond formed by the overlap of orbitals in a side-by-side fashion with the electron density concentrated above and below the plane of the nuclei of the bonding atoms. energy of isolated atoms bond order (H 2 molecule) = (2)-(0) 2 = 1 bond 1s b H H H H H H σ * = 1s a-1s b = antibonding MO = LCAO = linear combination of atomic orbitals node = zero electron density because of opposite phases ∆E = bond energy There is a big energy advantage for a hydrogen molecule over two hydrogen atoms. Bond order = (number of bonding electrons)-(number of antibonding electrons) 2 = amount of bonding 1s a hydrogen molecule = H 2 LUMO HOMO σ = 1s a + 1s b = bonding MO = potential energy higher, less stable lower, more stable LUMO = lowest unoccupied molecular orbital HOMO = highest occupied molecular orbital Similar phase of electron density (no node) adds together constructively.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
